Section 7.4
Defective Air Compressor
To determine if a defective air compressor is causing excessive oil consumption, perform the following:
- Perform a crankcase pressure test and record the test results;Refer to "2.1 Crankcase Pressure Test" .
- Disconnect the air discharge line from the air compressor. See Figure
"Air Line Attachments"
; refer to MBE 900 Service Manual
(6SE9007), special equipment chapter.
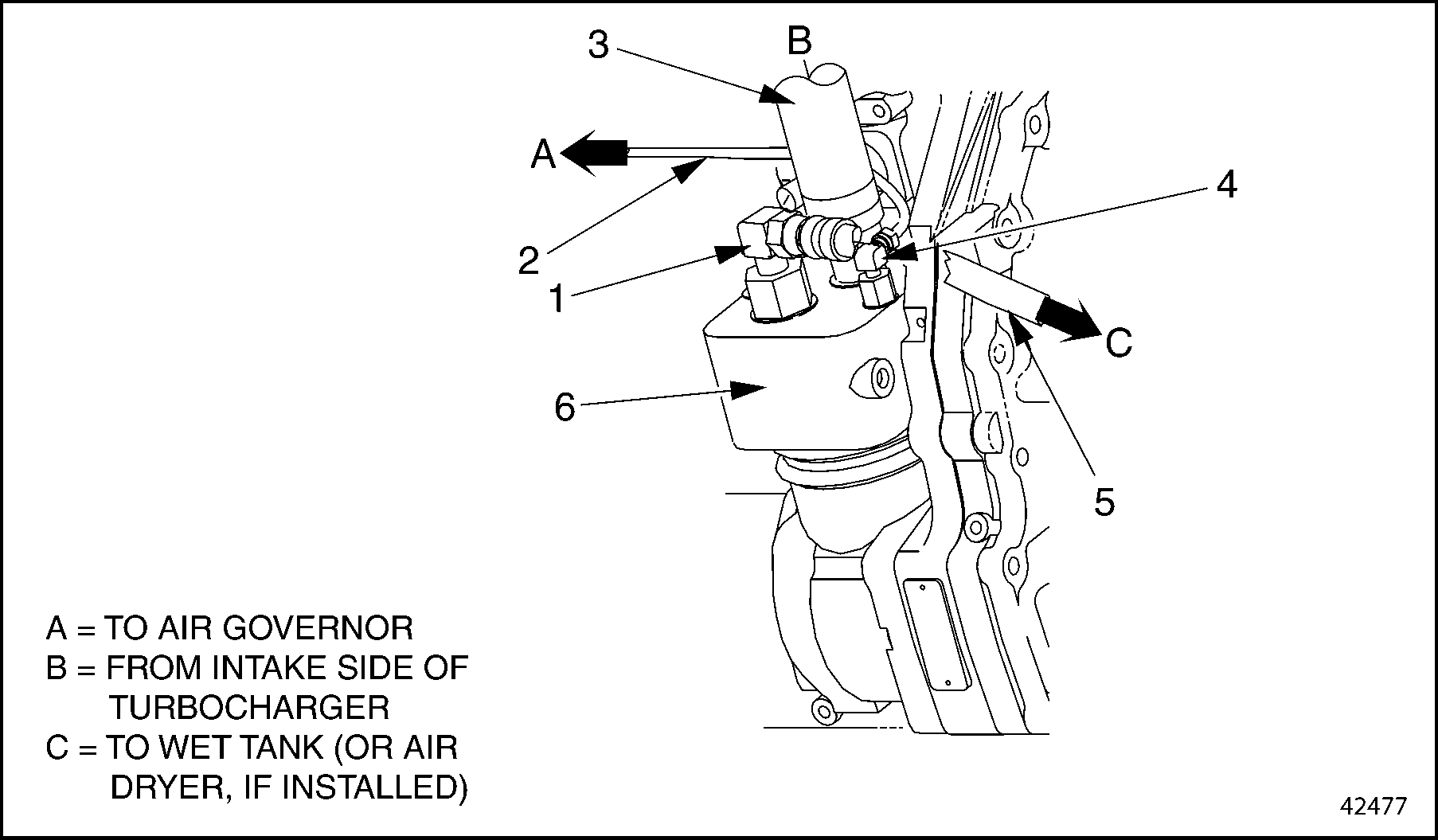
1. Discharge Port
4. Unloader Port
2. Unloader Air Line
5. Discharge Air Line
3. Intake Air Line
6. Air Compressor
Figure 1. Air Line Attachments
- Repeat step 1 and record the results.
- Compare the results of test one with test two.
- If the engine crankcase pressure remained the same, check the turbocharger; refer to "7.5 Defective Turbocharger" .
- If the engine crankcase pressure decreased, replace the air compressor; refer to MBE 900 Service Manual (6SE9007), special equipment chapter. Verify the replaced (or new) air compressor, refer to "7.4.1 Test Engine with Repaired Air Compressor" .
Section 7.4.1
Test Engine with Repaired Air Compressor
Perform the following steps to determine if the replaced (or new) air compressor resolved the excessive crankcase pressure:
|
PERSONAL INJURY |
|
To avoid injury before starting and running the engine, ensure the vehicle is parked on a level surface, parking brake is set, and the wheels are blocked. |
- Start and run the engine.
- Perform a crankcase pressure test; Refer to "2.1 Crankcase Pressure Test"
.
- If the engine crankcase pressure exceeds 0.62 kPa (2.5 in. H2 O), shut down the engine. Check for defective turbocharger. refer to "7.5 Defective Turbocharger" .
- If the engine crankcase pressure is within 0.62 kPa (2.5 in. H2 O), shut down the engine; no further troubleshooting is required.
| EPA07 MBE 900 DDEC VI Troubleshooting Guide - 6SE580 |
| Generated on 10-13-2008 |